
India's rail infrastructure is extensive, serving as a vital transportation backbone with over 68,000 km of track and a massive passenger and freight transport system. It's the fourth-largest railway network globally, connecting remote regions and urban centres, and is undergoing significant modernization and expansion projects.

Recent Government Initiatives
- Under the Union Budget 2025-26, the government allocated Rs. 3.02 lakh crore (US$ 34.7 billion) compared to Rs. 2.52 lakh crore (US$ 30.3 billion) in 2024-25 to the Ministry of Railways.
- Starting November 1, 2024, Indian Railways has revised its ticket booking rules by reducing the Advance Reservation Period (ARP) from 120 days to 60 days.
- As of January 2023, a total of 1,724 km of Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) had been commissioned, with 861 km completed on the Eastern DFC and 863 km on the Western DFC.
- The Union Cabinet announced an MoU with USAID/India (June 14, 2023) to help Indian Railways achieve Net Zero Carbon Emission by 2030.
- Indian Railways is proactively working towards Net Zero Carbon Emission by 2030, with several renewable energy and energy efficiency initiatives.
- Under the Union Budget 2023-24, a capital outlay of Rs. 2.40 lakh crore (US$ 29 billion) was allocated to the Ministry of Railways, the highest ever and about nine times the outlay made in 2013-14.
- The Bairabi-Sairang project aims to create an additional 51.38 km of railway track in northeast India.
- 100 PM-Gati Shakti Cargo Terminals for multimodal logistics facilities will be developed over the next three years.
- 2,000 km of network will be brought under Kavach, the indigenous technology for safety and capacity augmentation.
- The new & upgraded version of Vande Bharat Express between Gandhinagar Capital & Mumbai Central was inaugurated on September 30, 2022.
- Mission Raftaar launched for speed enhancement and to double the average speed of freight trains and increase the average speed of superfast/mail/express trains by 25 kmph.
- The government is developing a National Rail Plan to integrate the rail network with other modes of transport and develop a multi-modal transportation network.
- New Online Vendor Registration System launched by RDSO for digital and transparent systems and procedures.
- Plans to monetize assets including Dedicated Freight Corridors, induction of 150 modern rakes through PPP, station redevelopment, and more.

Indian Railway's Market & Performance
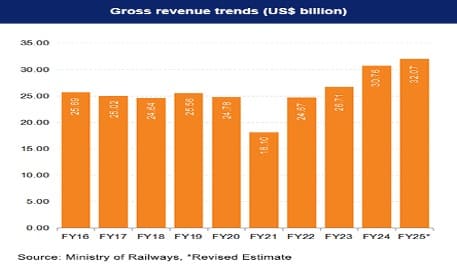
- Total revenue of Rs. 2.56 lakh crore (US$ 30.76 billion) by the end of FY24.
- Track laying of 5,100 km during FY24.
- Total number of passengers increased by 52 crore to reach 648 crore in FY 2023-24.
- Projected revenue of Rs. 2.78 lakh crore (US$ 32.07 billion) by the end of FY25*.
- Freight revenue estimated at Rs. 1,80,000 crore (US$ 20.7 billion) in FY25* (66% of traffic revenue).
- Passenger revenue at Rs. 80,000 crore (US$ 9.21 billion) in FY25*.
- Signalling and telecommunication upgrades: 15,000 km converted to automatic signalling, 37,000 km to be fitted with 'KAVACH' (Train Collision Avoidance System).
Key Features of India's Rail Infrastructure
- Extensive Network: Over 68,000 km of track, connecting various regions.
- Massive Passenger Traffic: Serving approximately 23 million passengers daily.
- Freight Movement: Significant role in goods movement across the nation.
- Electrification: Large portion of broad-gauge lines electrified for sustainability.
- Ongoing Development: Active investment in new lines, gauge conversions, and doubling projects.
- Safety Measures: Improvements in driver training and technology to reduce accidents.
- Future Outlook: Aiming to increase freight share, expand capacity, and achieve net-zero emissions by 2030.
Modernization and Expansion Initiatives
- Dedicated Freight Corridors: Improving freight efficiency and reducing congestion.
- Vande Bharat Trains: High-speed trains for improved passenger travel.
- Station Upgrades: Enhancing passenger experience and facilities.
- Electrification: Ongoing priority for efficiency and sustainability.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Safety: Addressing root causes of accidents, especially driver errors.
- Capacity: Meeting growing demand for passenger and freight transport.
- Sustainability: Commitment to reducing carbon footprint and adopting green technologies.
- Investment: Continued government and private sector investment is crucial.
In summary, Indian Railways is a vital and evolving infrastructure backbone, undergoing significant modernization and expansion to meet the growing needs of the nation's transportation and economic development.
